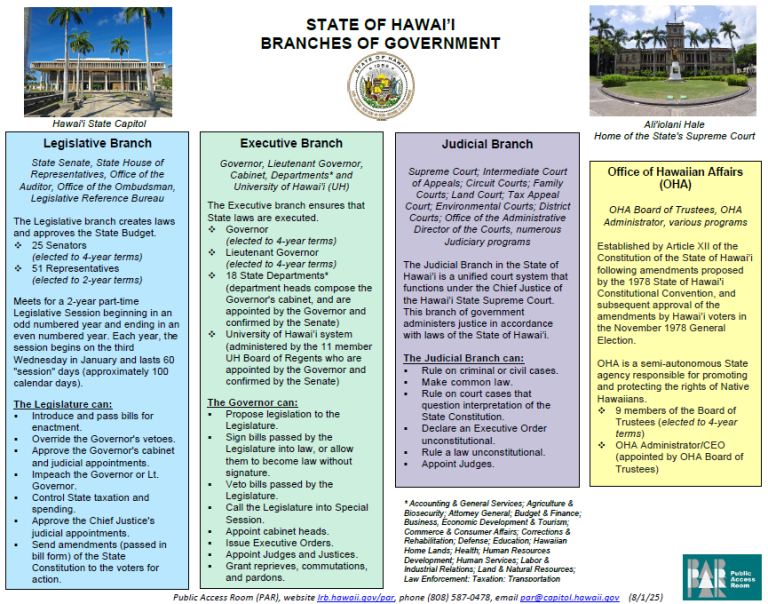
Overview of Branches of Government
Legislative Branch
State Senate, State House of Representatives, Office of the Auditor, Office of the Ombudsman, Legislative Reference Bureau.
The Legislative branch creates laws and approves the State Budget.
- 25 Senators (elected to 4-year terms)
- 51 Representatives (elected to 2-year terms)
Meets for a 2-year part-time Legislative Session beginning in an odd numbered year and ending in an even numbered year. Each year, the session begins on the third Wednesday in January and lasts 60 “session” days (approximately 100 calendar days).
The Legislature can:
- Introduce bills and pass bills for enactment.
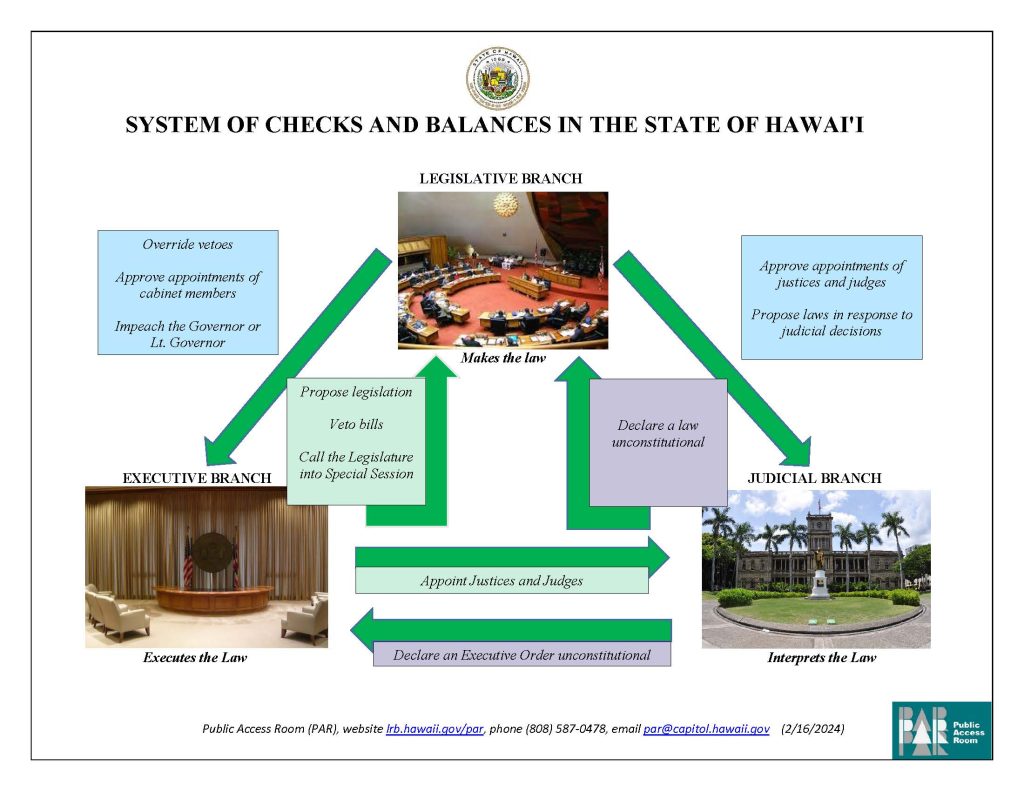
- Override the Governor’s vetoes.
- Approve the Governor’s cabinet and judicial appointments.
- Impeach the Governor or Lt. Governor.
- Control State taxation and spending.
- Approve the Chief Justice’s judicial appointments.
- Send amendments (passed in bill form) of the State Constitution to the voters for action.
Executive Branch
Governor, Lieutenant Governor, Cabinet, Departments* and University of Hawai’i (UH).
The Executive branch ensures that State laws are executed.
- Governor (elected to 4-year term)
- Lieutenant Governor (elected to 4-year term)
- State Departments* (department heads comprise the Governor’s cabinet, and are appointed by the Governor and confirmed by the Senate)
- University of Hawai’i system (administered by the 11 member UH Board of Regents who are appointed by the Governor and confirmed by the Senate)
The Governor can:
- Propose legislation to the Legislature.
- Sign bills passed by the Legislature into law, or allow them to become law without signature.
- Veto bills passed by the Legislature.
- Call the Legislature into Special Session.
- Appoint cabinet heads.
- Issue Executive Orders.
- Appoint Judges and Justices.
- Grant reprieves, commutations, and pardons.
*Departments include Accounting & General Services; Agriculture; Attorney General; Budget & Finance; Business, Economic Development & Tourism; Commerce & Consumer Affairs; Corrections and Rehabilitation; Defense; Education; Hawaiian Home Lands; Health; Human Resources Development; Human Services; Labor & Industrial Relations; Land & Natural Resources; Law Enforcement; Taxation; Transportation.
Judicial Branch
Supreme Court; Intermediate Court of Appeals; Circuit Courts; Family Courts; Land Court; Tax Appeal Court; Environmental Courts; District Courts; Office of the Administrative Director of the Courts, numerous Judiciary programs.
The Judicial Branch in the State of Hawai’i is a unified court system that functions under the Chief Justice of the Hawai’i State Supreme Court. This branch of government administers justice in accordance with laws of the State of Hawai’i.
The Judicial Branch can:
- Rule on criminal or civil cases.
- Make common law.
- Rule on court cases that question interpretation of the State Constitution.
- Declare an Executive Order unconstitutional.
- Rule a law unconstitutional.
- Appoint Judges.
Office of Hawaiian Affairs (OHA)
OHA Board of Trustees, OHA Administrator, various programs.
Established by Article XII of the Constitution of the State of Hawai’i following amendments proposed by the 1978 State of Hawai’i Constitutional Convention, and subsequent approval of the amendments by Hawai’i voters in the November 1978 General Election.
OHA is a semi-autonomous State agency responsible for promoting and protecting the rights of Native Hawaiians.
- 9 members of the Board of Trustees (elected to 4-year terms)
- OHA Administrator / CEO (appointed by OHA Board of Trustees)